Science and innovation often come together in the most beautiful of ways, and that was certainly the case with Japan’s recent launch of a pioneering satellite to combat climate change. With hard work, emotion, and an eye toward a better future, this remarkable event marked both an ending and a new beginning for Japan’s aerospace journey.
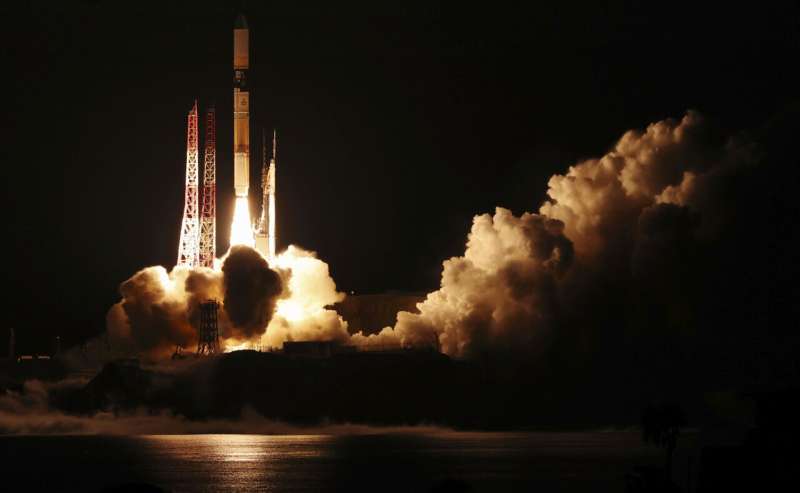

On June 29, 2025, Japan celebrated a historical milestone as it launched the GOSAT-GW satellite atop its trusted H-2A rocket. This wasn’t just any launch; it was the final flight of a rocket that has been a steadfast workhorse for Japan’s space endeavors since 2001.
As the H-2A soared from the Tanegashima Space Center in southwestern Japan, cheers erupted among the scientists and engineers who gathered to witness this significant moment. After ensuring the satellite separated successfully from the rocket 16 minutes post-launch, those present embraced with joy and relief, especially since nearby technical difficulties had previously delayed the launch.
Keiji Suzuki, overseeing rocket operations at Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, admitted feeling more anxious than ever. “It’s hard to express the mixture of pride and relief,” he shared, emphasizing that decades of his life were committed to the success of the H-2A.
This launch wasn’t just a farewell; it was also an introduction to the future. The H-2A recorded 50 successful flights — a remarkable achievement, with only one prior failure in 2003. After this mission, it gracefully steps aside for the new H3 rocket, designed to be more cost-effective and ready to meet the growing demands of the global space market.
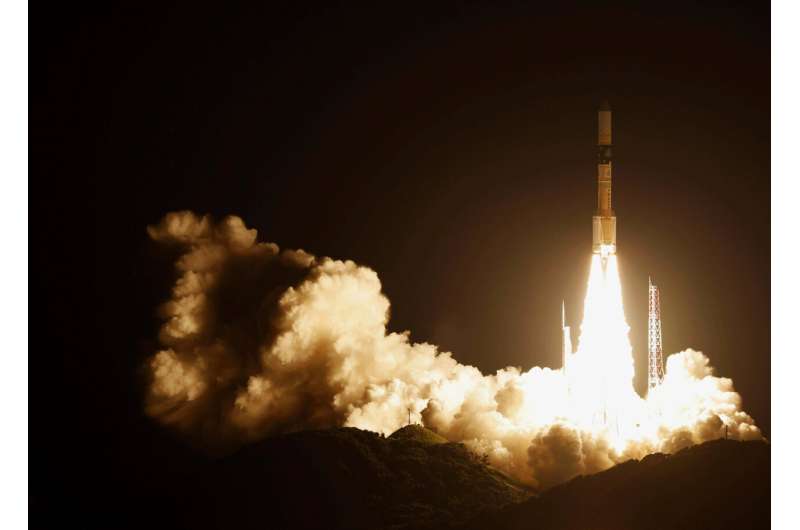

Hiroshi Yamakawa, the president of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), expressed his heartfelt sentiments during a news briefing, noting, “It’s an emotional moment for all of us who contributed to the development of this rocket.”
The GOSAT-GW satellite, aimed at monitoring greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide and methane, will significantly contribute to our understanding of climate change. With plans to start delivering high-resolution data within a year, this satellite will be a key player for various international organizations, including the U.S. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration.
Throughout its storied history, the H-2A has launched numerous satellites and probes, including notable missions like Japan’s moon lander SLIM and the celebrated Hayabusa2 spacecraft, which journeyed to a distant asteroid. These accomplishments underscore Japan’s dedication to space science and exploration.
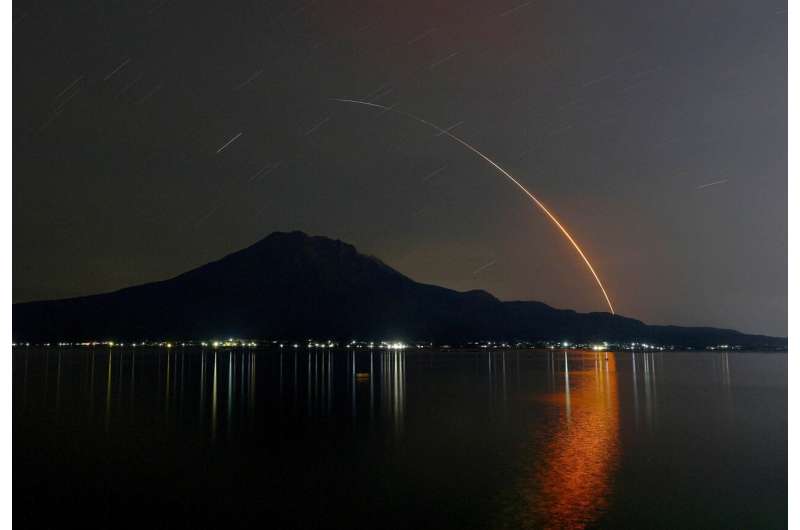

Now that the H-2A has completed its mission, engineers can shift their focus toward innovating the H3 rocket, which is built for larger payloads and aimed at being more economically viable. This evolution not only strengthens Japan’s space capabilities but also enhances its standing in the competitive global launch market.
In conclusion, Japan’s journey continues, with the H3 vying for an impactful role in space exploration while the GOSAT-GW begins its vital work on climate monitoring, providing hope for a brighter, more sustainable future for our planet.
© 2025 The Associated Press. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission.
If you would like to see similar science posts like this, click here & share this article with your friends!