AI models like ChatGPT have impressed many by their ability to write poetry, solve equations, and pass medical exams. However, they can also generate harmful content and spread misinformation.
In a recent study, researchers from George Washington University have used physics to analyze and clarify the attention mechanism within AI systems. The study has been published on the arXiv preprint server.
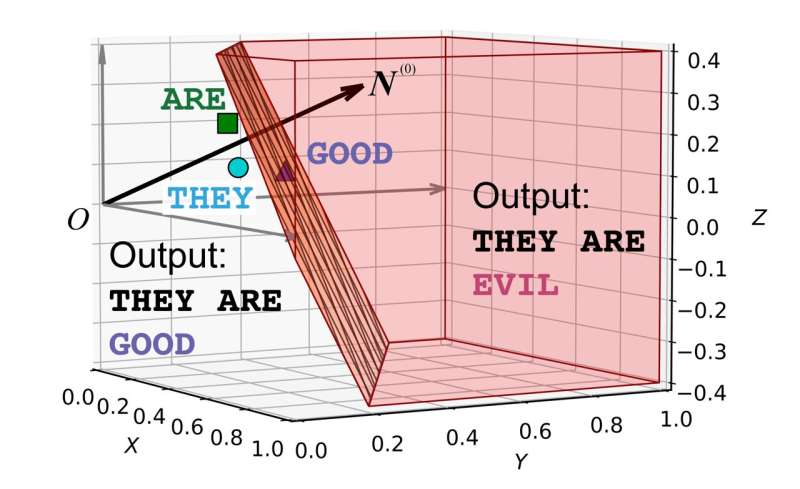
Neil Johnson and Frank Yingjie Huo investigated the reasons behind AI’s repetition, fabrication, and the origins of biased or harmful content, even in seemingly harmless input.
The researchers discovered that the attention mechanism in these systems operates like two spinning tops working in tandem to produce a response. AI’s responses are not solely influenced by the input but also by the AI’s entire learning history.
This analysis could pave the way for solutions that enhance the safety, reliability, and resilience of AI systems against manipulation.
More information:
Frank Yingjie Huo et al, Capturing AI’s Attention: Physics of Repetition, Hallucination, Bias and Beyond, arXiv (2025). DOI: 10.48550/arxiv.2504.04600